
NFT Verification Method Comparison Tool
Select a verification method below to compare its features and choose the best option for your artwork.
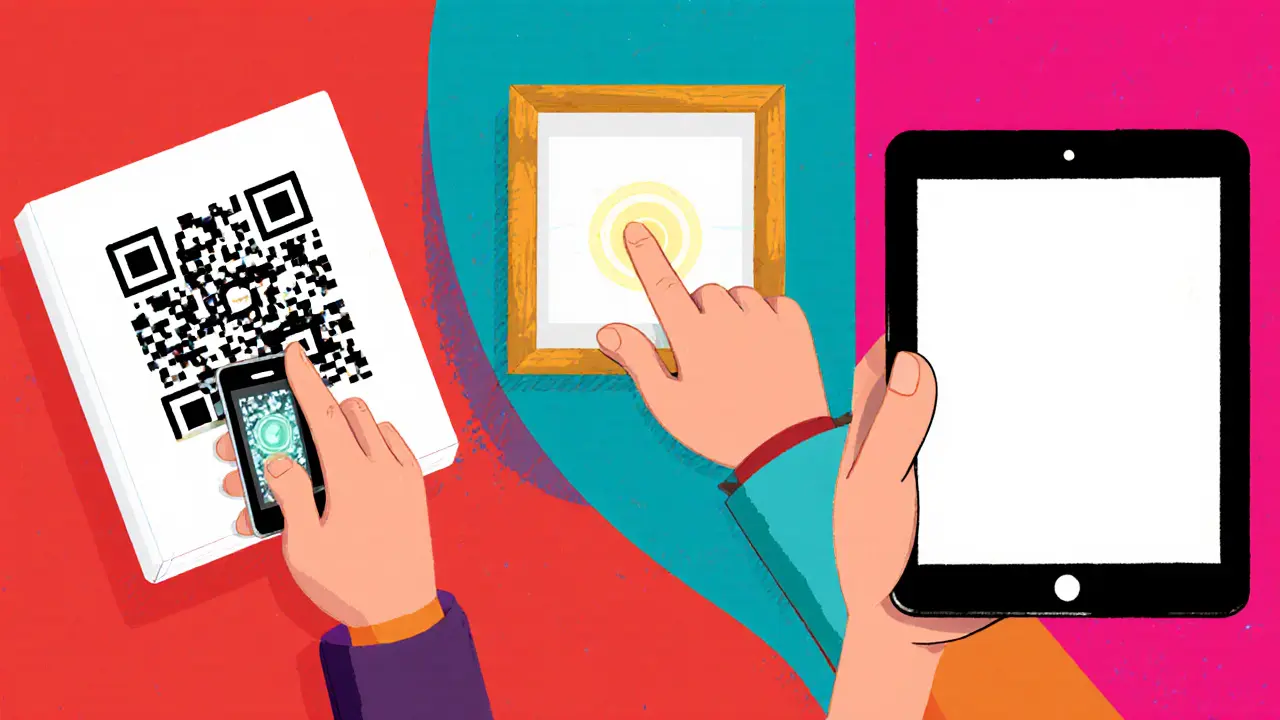
QR Code
Scan to verify ownership history
NFC Chip
Tap to read encrypted provenance
Digital Watermark
Detect invisible patterns
Cost
Device Requirement
Key Advantage
Which Method Should You Choose?
Digital Art Authentication with NFTs is the emerging process that uses non‑fungible tokens to prove who created a piece, who owns it now, and every hand it passed through. In a market where forgery drains an estimated $6billion a year, the promise of an immutable, instant‑check record feels like a lifeline.
What if you could scan a QR code on a canvas frame and see the entire ownership chain in seconds? That’s the reality for many collectors today, and it all hinges on digital art authentication powered by blockchain.
Why Traditional Certificates Fall Short
Paper certificates are vulnerable to tampering, loss, and outright fraud. A forger can copy a signature, replace a seal, or even alter the document’s wording. Because the record lives in a single location-usually an artist’s or gallery’s office-verifying it often requires phone calls, credential checks, and, frankly, a lot of patience.
By contrast, an NFT lives on a decentralized ledger. Once minted, the token’s metadata (artist name, creation date, provenance log) and the smart contract governing transfers are stored across thousands of nodes. No single party can rewrite that history without the network’s consensus, which in practice means it never happens.
Core Entities Behind NFT‑Based Authentication
- NFT is a unique digital token built on blockchain technology that represents ownership of a specific asset.
- Blockchain provides an immutable, time‑stamped ledger where every transaction is publicly auditable.
- Ethereum hosts roughly 72% of art‑related NFTs in 2025, offering robust smart‑contract capabilities.
- QR Code is a scannable matrix that links a physical artwork to its blockchain record.
- NFC chip embeds encrypted data inside a frame, readable by NFC‑enabled smartphones.
- Digital Watermark is an invisible pattern in the image file that points to the NFT’s metadata.
- Smart Contract automates ownership transfers and enforces royalty payments.
- Provenance is the documented history of ownership from creator to current holder.
Three Standard Verification Methods in 2025
| Method | How it works | Typical cost (USD) | Device requirement | Key advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QR Code | Scans to a URL that displays the token’s metadata and transaction history. | ~$2‑$5 per print | Any smartphone with a camera. | Instant, no extra hardware. |
| NFC Chip | Tap the frame to read encrypted provenance data stored on‑chain. | ~$8‑$12 per chip | NFC‑enabled phone or reader. | Tamper‑evident and works in low‑light environments. |
| Digital Watermark | Specialized app detects invisible pattern linking to the NFT. | ~$1‑$3 per file (software licence). | Smartphone or tablet with the app installed. | Works for purely digital artworks without physical media. |
All three methods pull the same blockchain record, so the choice often comes down to the artwork’s medium and the collector’s convenience.

Step‑by‑Step Workflow for Artists
- Set up a crypto wallet (MetaMask, Phantom, etc.).
- Choose a blockchain platform-Ethereum for high‑value pieces, Polygon or Solana for lower fees.
- Mint the NFT: upload the high‑resolution file, fill out metadata (artist name, title, creation date, edition size), and hit ‘Create.’
- Generate a verification token: the platform will give you a QR code, NFC tag, or watermark file.
- Attach the physical token (print QR, embed NFC chip, or embed watermark) to the artwork.
- Publish the token’s URL on your website and share with galleries.
- When the piece sells, the smart contract automatically updates the owner field and triggers any royalty clauses.
In practice the whole process takes a few hours for digitally fluent creators. For traditional painters, the learning curve stretches to 25‑40hours of training, but the payoff is a tamper‑proof provenance that can boost resale value by 10‑20% on average.
Benefits Over Paper Certificates
- Immutability: Once recorded, no one can alter the provenance trail.
- Transparency: Anyone with a wallet can view the full ownership chain.
- Decentralization: No single authority can block or erase records.
- Interoperability: Tokens move across marketplaces (OpenSea, Rarible, Foundation) without re‑issuance.
- Enhanced Security: Cryptographic signatures prevent forgery.
These advantages directly address the $6billion fraud problem highlighted by the FBI Art Crime Team.
Current Limitations and How to Overcome Them
While the tech is powerful, it isn’t a silver bullet. Three main hurdles still pop up:
- Internet Access: Verification needs an online connection. Galleries in remote locations often keep a cached copy of token metadata as a backup.
- Technical Comfort: 68% of collectors over 55 struggle with wallet setup. Peer‑to‑peer onboarding sessions run by galleries help bridge the gap.
- Blockchain Fees: Gas spikes on Ethereum can add $30‑$50 to a verification step. Layer‑2 solutions (Polygon, Optimism) now handle 95% of low‑value art transactions, keeping costs under $2.
Addressing these issues usually involves a hybrid approach: keep a traditional certificate as a secondary reference while the NFT handles the digital audit trail.

Best Practices From Industry Leaders
- Build an expert validation community - forums where curators, conservators, and artists can flag inconsistencies.
- Verify metadata at least twice using different blockchain explorers (Etherscan, Polygonscan).
- Use platform reputation scores; many marketplaces rank creators based on sales history and buyer reviews.
- Require a digital signature from the artist’s verified wallet before minting.
- Cross‑check the artwork on multiple platforms to catch duplicate token attempts.
Following these steps reduces the risk of accidental fraud and builds buyer confidence.
Regulatory Landscape in 2025
The EU’s MiCA (Markets in Crypto‑Assets) framework, active since December2024, forces NFT marketplaces to run KYC/AML checks on both sellers and buyers. That means any gallery selling a tokenized artwork must collect identity documents and report suspicious activity. While the added paperwork feels cumbersome, it also gives collectors a legal safety net-if a token turns out to be fraudulent, regulators can trace the wallet address back to a verified individual.
Future Outlook: From Niche to Standard
Gartner predicts 75% of high‑value art transactions will include blockchain authentication by 2027. New tech like biometric‑enabled NFC chips (VeriArt, 2025) and AI‑enhanced watermarks that adapt to canvas texture are already being piloted in major museums. However, experts such as Dr. Emily Watson remind us that “blockchain verifies the digital record, but it can’t replace a conservator’s eye for brush‑stroke analysis.” The most realistic scenario is a blended model where NFTs provide the immutable ledger, and human experts confirm the physical work’s authenticity.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does an NFT prove that a physical painting is genuine?
The NFT’s metadata contains a cryptographic hash of the artist’s digital signature and a description of the physical piece (size, medium, serial number). When a collector scans the QR code or NFC tag, the blockchain returns that hash, which can be matched to the artist’s original file. The hash can’t be altered, so the link between the digital token and the real-world artwork remains trustworthy.
Do I need a special wallet to verify an artwork?
A standard crypto wallet (MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Phantom) works. The verification app reads the public address stored in the QR code or NFC tag and pulls the token data from the blockchain. No private keys are needed for viewing.
What if the blockchain network is congested?
Most verification reads are free “view‑only” queries, so network congestion doesn’t raise fees. Only actions that modify the ledger (minting, transferring) incur gas costs, which can be avoided by using layer‑2 solutions or blockchains with lower fees like Polygon.
Can I sell a tokenized artwork on a traditional auction house?
Yes. Many major auction houses now accept NFTs as proof of provenance. The auction catalog includes the token ID and a QR code so buyers can instantly verify the chain of title.
What security risks should collectors watch for?
The biggest threat is losing the private key to the wallet that holds the NFT. Use hardware wallets, enable two‑factor authentication, and back up seed phrases offline. Phishing attacks account for 43% of NFT thefts, so verify URLs before entering credentials.




Comments (20)
Roxanne Maxwell
Really cool breakdown! I love how NFTs make provenance transparent-it’s like giving art its own digital birth certificate. My aunt just bought her first piece and she was terrified of scams, but scanning the QR code made her feel safe. That’s huge.
Jonathan Tanguay
Look i get it blockchain is cool but lets be real most of these NFTs are just jpeg files with a fancy url attached. The artist still has to sign the physical piece or its all just theater. You think some guy in Lagos is gonna scan a QR code to verify a Monet? Please. This is tech bro fantasy wrapped in a blockchain blanket. The real world still needs ink on paper and eyeballs on canvas. Stop pretending tech fixed art.
Elliott Algarin
It’s funny how we treat art like a stock ticker now. The blockchain tracks ownership but it doesn’t track soul. A brushstroke still carries the tremor of the hand that made it. Maybe the tech helps prevent fraud, but let’s not forget why we care about art in the first place-it’s not about who owns it, it’s about what it makes us feel. The NFT is a receipt, not the painting.
Ayanda Ndoni
bro this is so extra. why do i need a chip in my painting to know its real? just ask the artist. i swear people overcomplicate everything now. just hold the art, look at it, feel it. if it moves you, its real. no app needed.
Akinyemi Akindele Winner
Y’all acting like blockchain is the holy grail while the real fraud is you paying 50k for a JPEG that’s identical to the one you can screenshot for free. The only thing immutable here is your delusion. I’ve seen NFTs minted from AI-generated crap and sold as ‘originals.’ You’re not preserving art-you’re turning it into a crypto casino. The only thing decentralized is your common sense.
Ali Korkor
Don’t let the haters get you down. This is legit progress. Artists are finally getting paid when their work resells. That’s huge. If you’re nervous about tech, start small-mint one piece, try the QR code, see how it feels. You got this.
Serena Dean
Just did my first mint on Polygon-$1.20 in gas and I was done. Took me 20 mins. My cousin in Kenya just bought my piece using his phone. No bank. No gallery. Just art, moving freely. This is what freedom looks like.
Michael Folorunsho
Pathetic. You think a QR code makes your watercolor worth more? America’s obsession with digital vanity metrics is why art is dying. Real collectors don’t need blockchain-they know a masterpiece when they see it. This is just another Silicon Valley hustle to extract value from culture. You’re not preserving art. You’re commodifying grief.
Patrick De Leon
Irrelevant. The EU’s MiCA is the only thing keeping this from being a lawless free-for-all. Anyone who thinks blockchain alone prevents fraud is naive. Identity verification is non-negotiable. If you can’t prove who you are, you don’t own art-you own a glitch.
MANGESH NEEL
Let me tell you something about these NFTs-this is the new Ponzi scheme dressed in Web3 pajamas. Artists get tricked into minting while middlemen rake in 10% royalties forever. You think that’s fair? That’s slavery with a blockchain logo. And don’t even get me started on the environmental waste. You call this innovation? It’s ecological robbery with a whitepaper.
Sean Huang
They’re watching you. The blockchain isn’t secure-it’s a honeypot for the deep state. Every scan, every transaction, every wallet address is logged and fed into AI surveillance grids. You think they want you to own art? They want you to be tracked. The QR code? It’s a tracker. The NFC chip? A beacon. The watermark? A digital fingerprint for the surveillance state. Wake up. This isn’t freedom-it’s control with a crypto veneer.
Norman Woo
wait so if the server goes down or the blockchain gets hacked… then what? the qr code just leads to a 404 and your ‘authentic’ painting is just… a canvas? i mean… that’s kinda scary. who’s backing this up? like… really?
James Young
You missed the point entirely. The real innovation isn’t the QR code or the NFC chip-it’s the smart contract royalty system. Artists get paid every time their work flips. That’s never happened before. You think a painter in 1950 got a cut when their painting sold at Christie’s? No. So stop whining about tech and thank the blockchain for finally giving creators power.
Chloe Jobson
Hybrid models are the future. Physical certificate + NFT provenance. Redundancy isn’t weakness-it’s due diligence. Especially for high-value pieces. One system fails, the other holds. Simple.
Andrew Morgan
Just saw a 78-year-old lady in Santa Fe use her iPad to verify her husband’s painting. She cried. Said she finally understood why he spent so much time on this. That’s the real win. Not the tech. The connection it restored.
Gabrielle Loeser
While the technological infrastructure is commendable, it is imperative to recognize that the ontological essence of artistic authenticity remains inseparable from the materiality of the object itself. The blockchain may record provenance, but it cannot replicate the tactile resonance of pigment on linen.
Dick Lane
My brother’s a painter and he hates tech but he just minted his first piece. Said the royalties made him feel seen. That’s all that matters. The rest is noise.
John Murphy
What happens when the artist dies and no one has the private key? Who owns the NFT then? The estate? The platform? The blockchain doesn’t care about heirs. This is a legal nightmare waiting to happen
madhu belavadi
lol i just use instagram to prove my art is real. anyone who pays for this is a sucker.
Zach Crandall
Let’s not pretend this is democratization. The cost of entry-wallet setup, gas fees, understanding metadata-is a barrier for 90% of artists outside Silicon Valley. This isn’t inclusion. It’s exclusion with better marketing. The NFT is the new velvet rope.